XML documents form a tree structure that starts at "the root" and branches to "the leaves".
 An Example XML Document
An Example XML Document
XML documents use a self-describing and simple syntax:| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <note> <to>Tove</to> <from>Jani</from> <heading>Reminder</heading> <body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body> </note> |
The next line describes the root element of the document (like saying: "this document is a note"):
| <note> |
| <to>Tove</to> <from>Jani</from> <heading>Reminder</heading> <body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body> |
| </note> |
Don't you agree that XML is pretty self-descriptive?
 XML Documents Form a Tree Structure
XML Documents Form a Tree Structure
XML documents must contain a root element. This element is "the parent" of all other elements.The elements in an XML document form a document tree. The tree starts at the root and branches to the lowest level of the tree.
All elements can have sub elements (child elements):
| <root> <child> <subchild>.....</subchild> </child> </root> |
All elements can have text content and attributes (just like in HTML).
Example:
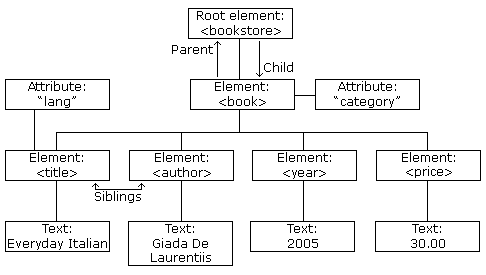 The image above represents one book in the XML below:
The image above represents one book in the XML below:| <bookstore> <book category="COOKING"> <title lang="en">Everyday Italian</title> <author>Giada De Laurentiis</author> <year>2005</year> <price>30.00</price> </book> <book category="CHILDREN"> <title lang="en">Harry Potter</title> <author>J K. Rowling</author> <year>2005</year> <price>29.99</price> </book> <book category="WEB"> <title lang="en">Learning XML</title> <author>Erik T. Ray</author> <year>2003</year> <price>39.95</price> </book> </bookstore> |
The <book> element has 4 children: <title>,< author>, <year>, <price>.